RunLoop学习整理
2016-09-21 » iOS开发基础关键词:
1、线程和 RunLoop 之间是一一对应的,其关系是保存在一个全局的 Dictionary 里
2、实际上 RunLoop 就是内部是一个 do-while 循环的这样一个函数
3、RunLoop 的核心是基于 mach port 的
4、App 启动后 RunLoop 的状态,系统默认注册了5个Mode
5、很多地方都有RunLoop的身影:AutoreleasePool、事件响应、定时器、PerformSelecter等
一、什么是RunLoop?
一般来讲,一个线程一次只能执行一个任务,执行完成后线程就会退出。如果我们需要一个机制,让线程能随时处理事件但并不退出,通常的代码逻辑是这样的:
function loop() {
initialize();
do {
var message = get_next_message();
process_message(message);
} while (message != quit);
}
这种模型通常被称作 Event Loop。 Event Loop 在很多系统和框架里都有实现,比如 Node.js 的事件处理,比如 Windows 程序的消息循环,再比如 OSX/iOS 里的 RunLoop。实现这种模型的关键点在于:
如何管理事件/消息,如何让线程在没有处理消息时休眠以避免资源占用、在有消息到来时立刻被唤醒。
所以,RunLoop 实际上就是一个对象,这个对象管理了其需要处理的事件和消息,并提供了一个入口函数来执行上面 Event Loop 的逻辑。线程执行了这个函数后,就会一直处于这个函数内部 “接受消息->等待->处理” 的循环中,直到这个循环结束(比如传入 quit 的消息),函数返回。
iOS 系统中,提供了两个这样的对象:NSRunLoop 和 CFRunLoopRef。
CFRunLoopRef 是在 CoreFoundation 框架内的,它提供了纯 C 函数的 API,所有这些 API 都是线程安全的。
NSRunLoop 是基于 CFRunLoopRef 的封装,提供了面向对象的 API,但是这些 API 不是线程安全的。
其实,工作中的大部分时间,我们是不怎么使用runloop的,了解runloop是怎么一回事,对问题发生后的处理、和对iOS系统的工作会有一个更深的认知。
这里整理一下什么是runloop,应该注意些什么,日常哪里的使用更多,iOS本身用他做了些什么。
为了理解runloop的意义,列举几个最接近日常开发的使用点:
1、最熟悉的定时器任务
2、基本都遇见的bug,scrollView滑动的时候计时器不走了
3、自动释放池的工作,一个运行循环是咋么样告诉释放池释放资源的
4、performSelecter的使用,事件是如何激活运行循环的
5、整个App中的运行循环是怎么样的
二、RunLoop与线程的关系
RunLoop的概念前面简单介绍了,平时我们涉及到RunLoop,那么就会涉及到线程,他们之间到底是什么关系?
苹果不允许直接创建 RunLoop,它只提供了两个自动获取的函数:CFRunLoopGetMain() 和 CFRunLoopGetCurrent()。 这两个函数内部的逻辑大概是下面这样:
/// 全局的Dictionary,key 是 pthread_t, value 是 CFRunLoopRef
static CFMutableDictionaryRef loopsDic;
/// 访问 loopsDic 时的锁
static CFSpinLock_t loopsLock;
/// 获取一个 pthread 对应的 RunLoop。
CFRunLoopRef _CFRunLoopGet(pthread_t thread) {
OSSpinLockLock(&loopsLock);
if (!loopsDic) {
// 第一次进入时,初始化全局Dic,并先为主线程创建一个 RunLoop。
loopsDic = CFDictionaryCreateMutable();
CFRunLoopRef mainLoop = _CFRunLoopCreate();
CFDictionarySetValue(loopsDic, pthread_main_thread_np(), mainLoop);
}
/// 直接从 Dictionary 里获取。
CFRunLoopRef loop = CFDictionaryGetValue(loopsDic, thread));
if (!loop) {
/// 取不到时,创建一个
loop = _CFRunLoopCreate();
CFDictionarySetValue(loopsDic, thread, loop);
/// 注册一个回调,当线程销毁时,顺便也销毁其对应的 RunLoop。
_CFSetTSD(..., thread, loop, __CFFinalizeRunLoop);
}
OSSpinLockUnLock(&loopsLock);
return loop;
}
CFRunLoopRef CFRunLoopGetMain() {
return _CFRunLoopGet(pthread_main_thread_np());
}
CFRunLoopRef CFRunLoopGetCurrent() {
return _CFRunLoopGet(pthread_self());
}
所以,线程和 RunLoop 之间是一一对应的,其关系是保存在一个全局的 Dictionary 里。线程刚创建时并没有 RunLoop,如果你不主动获取,那它一直都不会有。RunLoop 的创建是发生在第一次获取时,RunLoop 的销毁是发生在线程结束时。你只能在一个线程的内部获取其 RunLoop(主线程除外)。
三、详细了解RunLoop
我们查看 CoreFoundation 关于 RunLoop 对外的接口。
在 CoreFoundation 里面关于 RunLoop 有5个类:
CFRunLoopRef
CFRunLoopModeRef
CFRunLoopSourceRef
CFRunLoopTimerRef
CFRunLoopObserverRef
其中 CFRunLoopModeRef 类并没有对外暴露,只是通过 CFRunLoopRef 的接口进行了封装。他们的关系如下:

一个 RunLoop 包含若干个 Mode,每个 Mode 又包含若干个 Source / Timer / Observer。每次调用 RunLoop 的主函数时,只能指定其中一个 Mode,这个Mode被称作 CurrentMode。如果需要切换 Mode,只能退出 Loop,再重新指定一个 Mode 进入。这样做主要是为了分隔开不同组的 Source/Timer/Observer,让其互不影响。
那么它们各自是什么?
1、CFRunLoopSourceRef 是事件产生的地方
Source有两个版本:Source0 和 Source1。
source0:非port, 触摸事件,PerformSelectors
Source0 只包含了一个回调(函数指针),它并不能主动触发事件。使用时,你需要先调用
CFRunLoopSourceSignal(source),将这个 Source 标记为待处理,然后手动调用 CFRunLoopWakeUp(runloop) 来唤醒 RunLoop,让其处理这个事件。
<CFRunLoopSource 0x170160d80 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -1, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x0, callout = <redacted> (0x193c0bb5c)}}
source1:基于Port的线程间通信
Source1 包含了一个 mach_port 和一个回调(函数指针),被用于通过内核和其他线程相互发送消息。这种 Source 能主动唤醒 RunLoop 的线程
<CFRunLoopSource 0x174160cc0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFMachPort 0x174148770 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, port = 2203, source = 0x174160cc0, callout = <redacted> (0x1954dbfc8), context = <CFMachPort context 0x0>}}
2、CFRunLoopTimerRef 是基于时间的触发器
它和 NSTimer 是toll-free bridged 的,可以混用。其包含一个时间长度和一个回调(函数指针)。当其加入到 RunLoop 时,RunLoop会注册对应的时间点,当时间点到时,RunLoop会被唤醒以执行那个回调。
NSTimer 其实就是 CFRunLoopTimerRef。一个 NSTimer 注册到 RunLoop 后,RunLoop 会为其重复的时间点注册好事件。例如 10:00, 10:10, 10:20 这几个时间点。RunLoop为了节省资源,并不会在非常准确的时间点回调这个Timer。Timer 有个属性叫做 Tolerance (宽容度),标示了当时间点到后,容许有多少最大误差。
如果某个时间点被错过了,例如执行了一个很长的任务,则那个时间点的回调也会跳过去,不会延后执行。就比如等公交,如果 10:10 时我忙着玩手机错过了那个点的公交,那我只能等 10:20 这一趟了。
3、CFRunLoopObserverRef 是观察者
每个 Observer 都包含了一个回调(函数指针),当 RunLoop 的状态发生变化时,观察者就能通过回调接受到这个变化。可以观测的时间点有以下几个:
typedef CF_OPTIONS(CFOptionFlags, CFRunLoopActivity) {
kCFRunLoopEntry = (1UL << 0), // 即将进入Loop
kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers = (1UL << 1), // 即将处理 Timer
kCFRunLoopBeforeSources = (1UL << 2), // 即将处理 Source
kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting = (1UL << 5), // 即将进入休眠
kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting = (1UL << 6), // 刚从休眠中唤醒
kCFRunLoopExit = (1UL << 7), // 即将退出Loop
};
我们可以使用 CoreFoundation 提供的方法去自行检测这些观察者, 后面实验部分会详细描述以上部分。
上面的 Source/ Timer/ Observer 被统称为 mode item
1、一个 item 可以被同时加入多个 mode,但一个 item 被重复加入同一个 mode 时是不会有效果的。
2、如果一个 mode 中一个 item 都没有,则 RunLoop 会直接退出,不进入循环。
3、如果mode中只有观察者 也不会进入循环。
4、我们看一看 RunLoop 和 RunLoopMode 的构成
CFRunLoopMode 和 CFRunLoop 的结构大致如下:
struct __CFRunLoopMode {
CFStringRef _name; // Mode Name, 例如 @"kCFRunLoopDefaultMode"
CFMutableSetRef _sources0; // Set
CFMutableSetRef _sources1; // Set
CFMutableArrayRef _observers; // Array
CFMutableArrayRef _timers; // Array
...
};
struct __CFRunLoop {
CFMutableSetRef _commonModes; // Set
CFMutableSetRef _commonModeItems; // Set<Source/Observer/Timer>
CFRunLoopModeRef _currentMode; // Current Runloop Mode
CFMutableSetRef _modes; // Set
...
};
5、操作管理 RunLoopMode
__CFRunLoop有个概念叫 “CommonModes”,一个 Mode 可以将自己标记为 “Common” 属性
将其 modeName 添加到 RunLoop 的 “CommonModes” 中。每当 RunLoop 的内容发生变化时,RunLoop 都会自动将 _commonModeItems 里的 Source/Observer/Timer 同步到具有 “Common” 标记的所有Mode里。
打印出来的RunLoop可以看到 CommonModes 中的 ModeName
common modes = <CFBasicHash 0x17004bfa0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable set, count = 2,
entries =>
0 : <CFString 0x1b2d00970 [0x1b843cbb8]>{contents = "UITrackingRunLoopMode"}
2 : <CFString 0x1b22484b0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{contents = "kCFRunLoopDefaultMode"}
}
应用场景举例:
主线程的 RunLoop 里有两个预置的 Mode:kCFRunLoopDefaultMode 和 UITrackingRunLoopMode (也就是苹果公开提供的两个Mode)。
这两个 Mode 都已经被标记为 “Common” 属性。DefaultMode 是 App 平时所处的状态,TrackingRunLoopMode 是追踪 ScrollView 滑动时的状态。当你创建一个 Timer 并加到 DefaultMode 时,Timer 会得到重复回调,但此时滑动一个TableView时,RunLoop 会将 mode 切换为 TrackingRunLoopMode,这时 Timer 就不会被回调,并且也不会影响到滑动操作。
这个时候其实你需要一个 Timer,在两个 Mode 中都能得到回调
一种办法就是将这个 Timer 分别加入这两个 Mode。
还有一种方式,就是将 Timer 加入到顶层的 RunLoop 的 “commonModeItems” 中。”commonModeItems” 被 RunLoop 自动更新到所有具有”Common”属性的 Mode 里去。
1、NSTimer的使用:
NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1 target:self selector:@selector(wantTodo) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
//timerWith开头的方法创建的Timer如果不加下面一句无法运行。
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
2、NSTimer和scrollView的冲突问题
把timer加到NSRunLoopCommonModes,那么两个mode都会被分配,这样两种mode下都可以执行了。
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:self.timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];
CFRunLoop对外暴露的管理 Mode 接口只有下面2个:
CFRunLoopAddCommonMode(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopMode mode);
CFRunLoopRunInMode(CFRunLoopMode mode, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean returnAfterSourceHandled);
Mode 暴露的管理 mode item 的接口有下面几个:
CFRunLoopAddSource(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopSourceRef source, CFRunLoopMode mode);
CFRunLoopRemoveSource(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopSourceRef source, CFRunLoopMode mode);
CFRunLoopAddObserver(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopObserverRef observer, CFRunLoopMode mode);
CFRunLoopRemoveObserver(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopObserverRef observer, CFRunLoopMode mode);
CFRunLoopAddTimer(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopTimerRef timer, CFRunLoopMode mode);
CFRunLoopRemoveTimer(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopTimerRef timer, CFRunLoopMode mode);
对于一个 RunLoop 来说,其内部的 mode 只能增加不能删除。
3、NSTimer和ViewController的循环引用
4、事件源的mode需要和当前runloop的mode 一致才会进入循环。(比如添加一个事件源到UITrackingRunLoopMode,但是runloop默认是NSDefaultRunLoopMode)
6、RunLoop 的内部逻辑 与 底层实现
RunLoop 的内部逻辑
根据苹果在文档里的说明,RunLoop 内部的逻辑大致如下:
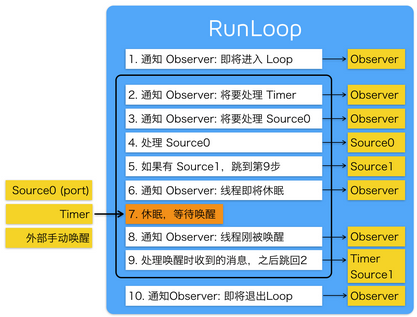
/// 用DefaultMode启动
void CFRunLoopRun(void) {
CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), kCFRunLoopDefaultMode, 1.0e10, false);
}
/// 用指定的Mode启动,允许设置RunLoop超时时间
int CFRunLoopRunInMode(CFStringRef modeName, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean stopAfterHandle) {
return CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), modeName, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled);
}
/// RunLoop的实现
int CFRunLoopRunSpecific(runloop, modeName, seconds, stopAfterHandle) {
/// 首先根据modeName找到对应mode
CFRunLoopModeRef currentMode = __CFRunLoopFindMode(runloop, modeName, false);
/// 如果mode里没有source/timer/observer, 直接返回。
if (__CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(currentMode)) return;
/// 1. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 即将进入 loop。
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopEntry);
/// 内部函数,进入loop
__CFRunLoopRun(runloop, currentMode, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled) {
Boolean sourceHandledThisLoop = NO;
int retVal = 0;
do {
/// 2. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 即将触发 Timer 回调。
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers);
/// 3. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 即将触发 Source0 (非port) 回调。
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopBeforeSources);
/// 执行被加入的block
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(runloop, currentMode);
/// 4. RunLoop 触发 Source0 (非port) 回调。
sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSources0(runloop, currentMode, stopAfterHandle);
/// 执行被加入的block
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(runloop, currentMode);
/// 5. 如果有 Source1 (基于port) 处于 ready 状态,直接处理这个 Source1 然后跳转去处理消息。
if (__Source0DidDispatchPortLastTime) {
Boolean hasMsg = __CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(dispatchPort, &msg)
if (hasMsg) goto handle_msg;
}
/// 通知 Observers: RunLoop 的线程即将进入休眠(sleep)。
if (!sourceHandledThisLoop) {
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting);
}
/// 7. 调用 mach_msg 等待接受 mach_port 的消息。线程将进入休眠, 直到被下面某一个事件唤醒。
/// • 一个基于 port 的Source 的事件。
/// • 一个 Timer 到时间了
/// • RunLoop 自身的超时时间到了
/// • 被其他什么调用者手动唤醒
__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(waitSet, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort) {
mach_msg(msg, MACH_RCV_MSG, port); // thread wait for receive msg
}
/// 8. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 的线程刚刚被唤醒了。
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(runloop, currentMode, kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting);
/// 收到消息,处理消息。
handle_msg:
/// 9.1 如果一个 Timer 到时间了,触发这个Timer的回调。
if (msg_is_timer) {
__CFRunLoopDoTimers(runloop, currentMode, mach_absolute_time())
}
/// 9.2 如果有dispatch到main_queue的block,执行block。
else if (msg_is_dispatch) {
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__(msg);
}
/// 9.3 如果一个 Source1 (基于port) 发出事件了,处理这个事件
else {
CFRunLoopSourceRef source1 = __CFRunLoopModeFindSourceForMachPort(runloop, currentMode, livePort);
sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSource1(runloop, currentMode, source1, msg);
if (sourceHandledThisLoop) {
mach_msg(reply, MACH_SEND_MSG, reply);
}
}
/// 执行加入到Loop的block
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(runloop, currentMode);
if (sourceHandledThisLoop && stopAfterHandle) {
/// 进入loop时参数说处理完事件就返回。
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunHandledSource;
} else if (timeout) {
/// 超出传入参数标记的超时时间了
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunTimedOut;
} else if (__CFRunLoopIsStopped(runloop)) {
/// 被外部调用者强制停止了
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunStopped;
} else if (__CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(runloop, currentMode)) {
/// source/timer/observer一个都没有了
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunFinished;
}
/// 如果没超时,mode里没空,loop也没被停止,那继续loop。
} while (retVal == 0);
}
/// 10. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 即将退出。
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, currentMode, kCFRunLoopExit);
}
可以看到,实际上 RunLoop 就是这样一个函数,其内部是一个 do-while 循环。当你调用 CFRunLoopRun() 时,线程就会一直停留在这个循环里;直到超时或被手动停止,该函数才会返回。
RunLoop 的底层实现
RunLoop 的核心是基于 mach port 的。
RunLoop 的核心就是一个 mach_msg() (见上面代码的第7步),RunLoop 调用这个函数去接收消息,如果没有别人发送 port 消息过来,内核会将线程置于等待状态。例如你在模拟器里跑起一个 iOS 的 App,然后在 App 静止时点击暂停,你会看到主线程调用栈是停留在 mach_msg_trap() 这个地方。
具体细节可以看大佬文章:深入理解runloop
四、系统用 RunLoop 实现的功能
1、App 启动后 RunLoop 的状态,系统默认注册了5个Mode
首先我们根据后面实验得到的启动是构建的RunLoop的,可以看一下 App 启动后 RunLoop 的状态:
CFRunLoop {
current mode = kCFRunLoopDefaultMode
common modes = {
UITrackingRunLoopMode
kCFRunLoopDefaultMode
}
common mode items = {
// source0 (manual)
CFRunLoopSource {order =-1, {
callout = _UIApplicationHandleEventQueue}}
CFRunLoopSource {order =-1, {
callout = PurpleEventSignalCallback }}
CFRunLoopSource {order = 0, {
callout = FBSSerialQueueRunLoopSourceHandler}}
// source1 (mach port)
CFRunLoopSource {order = 0, {port = 17923}}
CFRunLoopSource {order = 0, {port = 12039}}
CFRunLoopSource {order = 0, {port = 16647}}
CFRunLoopSource {order =-1, {
callout = PurpleEventCallback}}
CFRunLoopSource {order = 0, {port = 2407,
callout = _ZL20notify_port_callbackP12__CFMachPortPvlS1_}}
CFRunLoopSource {order = 0, {port = 1c03,
callout = __IOHIDEventSystemClientAvailabilityCallback}}
CFRunLoopSource {order = 0, {port = 1b03,
callout = __IOHIDEventSystemClientQueueCallback}}
CFRunLoopSource {order = 1, {port = 1903,
callout = __IOMIGMachPortPortCallback}}
// Ovserver
CFRunLoopObserver {order = -2147483647, activities = 0x1, // Entry
callout = _wrapRunLoopWithAutoreleasePoolHandler}
CFRunLoopObserver {order = 0, activities = 0x20, // BeforeWaiting
callout = _UIGestureRecognizerUpdateObserver}
CFRunLoopObserver {order = 1999000, activities = 0xa0, // BeforeWaiting | Exit
callout = _afterCACommitHandler}
CFRunLoopObserver {order = 2000000, activities = 0xa0, // BeforeWaiting | Exit
callout = _ZN2CA11Transaction17observer_callbackEP19__CFRunLoopObservermPv}
CFRunLoopObserver {order = 2147483647, activities = 0xa0, // BeforeWaiting | Exit
callout = _wrapRunLoopWithAutoreleasePoolHandler}
// Timer
CFRunLoopTimer {firing = No, interval = 3.1536e+09, tolerance = 0,
next fire date = 453098071 (-4421.76019 @ 96223387169499),
callout = _ZN2CAL14timer_callbackEP16__CFRunLoopTimerPv (QuartzCore.framework)}
},
modes = {
CFRunLoopMode {
sources0 = { /* same as 'common mode items' */ },
sources1 = { /* same as 'common mode items' */ },
observers = { /* same as 'common mode items' */ },
timers = { /* same as 'common mode items' */ },
},
CFRunLoopMode {
sources0 = { /* same as 'common mode items' */ },
sources1 = { /* same as 'common mode items' */ },
observers = { /* same as 'common mode items' */ },
timers = { /* same as 'common mode items' */ },
},
CFRunLoopMode {
sources0 = {
CFRunLoopSource {order = 0, {
callout = FBSSerialQueueRunLoopSourceHandler}}
},
sources1 = (null),
observers = {
CFRunLoopObserver >{activities = 0xa0, order = 2000000,
callout = _ZN2CA11Transaction17observer_callbackEP19__CFRunLoopObservermPv}
)},
timers = (null),
},
CFRunLoopMode {
sources0 = {
CFRunLoopSource {order = -1, {
callout = PurpleEventSignalCallback}}
},
sources1 = {
CFRunLoopSource {order = -1, {
callout = PurpleEventCallback}}
},
observers = (null),
timers = (null),
},
CFRunLoopMode {
sources0 = (null),
sources1 = (null),
observers = (null),
timers = (null),
}
}
}
App 启动后 RunLoop 的状态,系统默认注册了5个Mode:
- kCFRunLoopDefaultMode: App的默认 Mode,通常主线程是在这个 Mode 下运行的。
- UITrackingRunLoopMode: 界面跟踪 Mode,用于 ScrollView 追踪触摸滑动,保证界面滑动时不受其他 Mode 影响。
- UIInitializationRunLoopMode: 在刚启动 App 时第进入的第一个 Mode,启动完成后就不再使用。
- GSEventReceiveRunLoopMode: 接受系统事件的内部 Mode,通常用不到。
- kCFRunLoopCommonModes: 这是一个占位的 Mode,没有实际作用。
当 RunLoop 进行回调时,一般都是通过一个很长的函数调用出去 (call out), 当你在你的代码中下断点调试时,通常能在调用栈上看到这些函数。下面是这几个函数的整理版本,如果你在调用栈中看到这些长函数名,在这里查找一下就能定位到具体的调用地点了:
/// 1. 通知Observers,即将进入RunLoop
/// 此处有Observer会创建AutoreleasePool: _objc_autoreleasePoolPush();
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_AN_OBSERVER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION__(kCFRunLoopEntry);
do {
/// 2. 通知 Observers: 即将触发 Timer 回调。
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_AN_OBSERVER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION__(kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers);
/// 3. 通知 Observers: 即将触发 Source (非基于port的,Source0) 回调。
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_AN_OBSERVER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION__(kCFRunLoopBeforeSources);
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_BLOCK__(block);
/// 4. 触发 Source0 (非基于port的) 回调。
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_SOURCE0_PERFORM_FUNCTION__(source0);
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_BLOCK__(block);
/// 6. 通知Observers,即将进入休眠
/// 此处有Observer释放并新建AutoreleasePool: _objc_autoreleasePoolPop(); _objc_autoreleasePoolPush();
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_AN_OBSERVER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION__(kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting);
/// 7. sleep to wait msg.
mach_msg() -> mach_msg_trap();
/// 8. 通知Observers,线程被唤醒
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_AN_OBSERVER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION__(kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting);
/// 9. 如果是被Timer唤醒的,回调Timer
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_TIMER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION__(timer);
/// 9. 如果是被dispatch唤醒的,执行所有调用 dispatch_async 等方法放入main queue 的 block
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__(dispatched_block);
/// 9. 如果如果Runloop是被 Source1 (基于port的) 的事件唤醒了,处理这个事件
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_SOURCE1_PERFORM_FUNCTION__(source1);
} while (...);
/// 10. 通知Observers,即将退出RunLoop
/// 此处有Observer释放AutoreleasePool: _objc_autoreleasePoolPop();
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_AN_OBSERVER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION__(kCFRunLoopExit);
2、AutoreleasePool
RunLoop开始的时候,自动释放池创建、对象放入自动释放池,RunLoop进入休眠或者结束的时候 自动释放池释放并创建新的自动释放池,等待下一个循环。
3、事件响应
UIEvent 的处理或分发,其中包括识别 UIGesture/处理屏幕旋转/发送给 UIWindow 等。通常事件比如 UIButton 点击、touchesBegin/Move/End/Cancel 事件都是监听回调中完成的,也是runloop。
4、手势识别
当上面的 _UIApplicationHandleEventQueue() 识别了一个手势时,其首先会调用 Cancel 将当前的 touchesBegin/Move/End 系列回调打断。随后系统将对应的 UIGestureRecognizer 标记为待处理。
苹果注册了一个 Observer 监测 BeforeWaiting (Loop即将进入休眠) 事件,这个Observer的回调函数是 _UIGestureRecognizerUpdateObserver(),其内部会获取所有刚被标记为待处理的 GestureRecognizer,并执行GestureRecognizer的回调。
当有 UIGestureRecognizer 的变化(创建/销毁/状态改变)时,这个回调都会进行相应处理。
5、界面更新
系统注册的监听者,遍历所有待处理的 UIView/CAlayer 以执行实际的绘制和调整,并更新 UI 界面。
6、定时器
NSTimer 其实就是 CFRunLoopTimerRef,他们之间是 toll-free bridged 的。一个 NSTimer 注册到 RunLoop 后,RunLoop 会为其重复的时间点注册好事件。例如 10:00, 10:10, 10:20 这几个时间点。RunLoop为了节省资源,并不会在非常准确的时间点回调这个Timer。Timer 有个属性叫做 Tolerance (宽容度),标示了当时间点到后,容许有多少最大误差。
如果某个时间点被错过了,例如执行了一个很长的任务,则那个时间点的回调也会跳过去,不会延后执行。就比如等公交,如果 10:10 时我忙着玩手机错过了那个点的公交,那我只能等 10:20 这一趟了。
7、PerformSelecter
当调用 NSObject 的 performSelecter:afterDelay: 后,实际上其内部会创建一个 Timer 并添加到当前线程的 RunLoop 中。所以如果当前线程没有 RunLoop,则这个方法会失效。
当调用 performSelector:onThread: 时,实际上其会创建一个 Timer 加到对应的线程去,同样的,如果对应线程没有 RunLoop 该方法也会失效。
8、GCD
当调用 dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), block) 时,libDispatch 会向主线程的 RunLoop 发送消息,RunLoop会被唤醒,并从消息中取得这个 block,并在回调 CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE() 里执行这个 block。但这个逻辑仅限于 dispatch 到主线程,dispatch 到其他线程仍然是由 libDispatch 处理的。
9、网络请求
iOS 中,关于网络请求的接口自下至上有如下几层:
CFSocket
CFNetwork ->ASIHttpRequest
NSURLConnection ->AFNetworking
NSURLSession ->AFNetworking2, Alamofire
CFSocket 是最底层的接口,只负责 socket 通信。 CFNetwork 是基于 CFSocket 等接口的上层封装,ASIHttpRequest 工作于这一层。 NSURLConnection 是基于 CFNetwork 的更高层的封装,提供面向对象的接口,AFNetworking 工作于这一层。 NSURLSession 是 iOS7 中新增的接口,表面上是和 NSURLConnection 并列的,但底层仍然用到了 NSURLConnection 的部分功能 (比如 com.apple.NSURLConnectionLoader 线程),AFNetworking2 和 Alamofire 工作于这一层。 下面主要介绍下 NSURLConnection 的工作过程。
通常使用 NSURLConnection 时,你会传入一个 Delegate,当调用了 [connection start] 后,这个 Delegate 就会不停收到事件回调。实际上,start 这个函数的内部会会获取 CurrentRunLoop,然后在其中的 DefaultMode 添加了4个 Source0 (即需要手动触发的Source)。CFMultiplexerSource 是负责各种 Delegate 回调的,CFHTTPCookieStorage 是处理各种 Cookie 的。
当开始网络传输时,我们可以看到 NSURLConnection 创建了两个新线程:com.apple.NSURLConnectionLoader 和 com.apple.CFSocket.private。其中 CFSocket 线程是处理底层 socket 连接的。NSURLConnectionLoader 这个线程内部会使用 RunLoop 来接收底层 socket 的事件,并通过之前添加的 Source0 通知到上层的 Delegate。
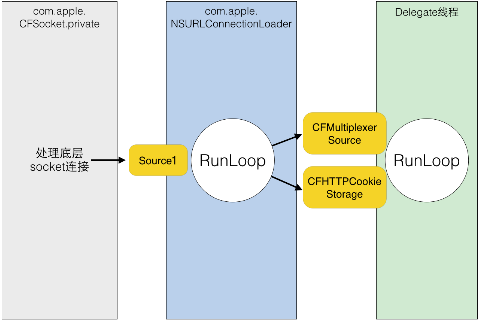
NSURLConnectionLoader 中的 RunLoop 通过一些基于 mach port 的 Source 接收来自底层 CFSocket 的通知。当收到通知后,其会在合适的时机向 CFMultiplexerSource 等 Source0 发送通知,同时唤醒 Delegate 线程的 RunLoop 来让其处理这些通知。CFMultiplexerSource 会在 Delegate 线程的 RunLoop 对 Delegate 执行实际的回调。
AFNetworking中RunLoop运用
AFURLConnectionOperation 这个类是基于 NSURLConnection 构建的,其希望能在后台线程接收 Delegate 回调。为此 AFNetworking 单独创建了一个线程,并在这个线程中启动了一个 RunLoop:
+ (void)networkRequestThreadEntryPoint:(id)__unused object {
@autoreleasepool {
[[NSThread currentThread] setName:@"AFNetworking"];
NSRunLoop *runLoop = [NSRunLoop currentRunLoop];
[runLoop addPort:[NSMachPort port] forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
[runLoop run];
}
}
+ (NSThread *)networkRequestThread {
static NSThread *_networkRequestThread = nil;
static dispatch_once_t oncePredicate;
dispatch_once(&oncePredicate, ^{
_networkRequestThread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(networkRequestThreadEntryPoint:) object:nil];
[_networkRequestThread start];
});
return _networkRequestThread;
}
RunLoop 启动前内部必须要有至少一个 Timer/Observer/Source,所以 AFNetworking 在 [runLoop run] 之前先创建了一个新的 NSMachPort 添加进去了。通常情况下,调用者需要持有这个 NSMachPort (mach_port) 并在外部线程通过这个 port 发送消息到 loop 内;但此处添加 port 只是为了让 RunLoop 不至于退出,并没有用于实际的发送消息。
- (void)start {
[self.lock lock];
if ([self isCancelled]) {
[self performSelector:@selector(cancelConnection) onThread:[[self class] networkRequestThread] withObject:nil waitUntilDone:NO modes:[self.runLoopModes allObjects]];
} else if ([self isReady]) {
self.state = AFOperationExecutingState;
[self performSelector:@selector(operationDidStart) onThread:[[self class] networkRequestThread] withObject:nil waitUntilDone:NO modes:[self.runLoopModes allObjects]];
}
[self.lock unlock];
}
当需要这个后台线程执行任务时,AFNetworking 通过调用 [NSObject performSelector:onThread:..] 将这个任务扔到了后台线程的 RunLoop 中。
AsyncDisplayKit
AsyncDisplayKit 是 Facebook 推出的用于保持界面流畅性的框架,其原理大致如下:
UI 线程中一旦出现繁重的任务就会导致界面卡顿,这类任务通常分为3类:排版,绘制,UI对象操作。
排版通常包括计算视图大小、计算文本高度、重新计算子式图的排版等操作。
绘制一般有文本绘制 (例如 CoreText)、图片绘制 (例如预先解压)、元素绘制 (Quartz)等操作。
UI对象操作通常包括 UIView/CALayer 等 UI 对象的创建、设置属性和销毁。
其中前两类操作可以通过各种方法扔到后台线程执行,而最后一类操作只能在主线程完成,并且有时后面的操作需要依赖前面操作的结果 (例如TextView创建时可能需要提前计算出文本的大小)。ASDK 所做的,就是尽量将能放入后台的任务放入后台,不能的则尽量推迟 (例如视图的创建、属性的调整)。
为此,ASDK 创建了一个名为 ASDisplayNode 的对象,并在内部封装了 UIView/CALayer,它具有和 UIView/CALayer 相似的属性,例如 frame、backgroundColor等。所有这些属性都可以在后台线程更改,开发者可以只通过 Node 来操作其内部的 UIView/CALayer,这样就可以将排版和绘制放入了后台线程。但是无论怎么操作,这些属性总需要在某个时刻同步到主线程的 UIView/CALayer 去。
ASDK 仿照 QuartzCore/UIKit 框架的模式,实现了一套类似的界面更新的机制:即在主线程的 RunLoop 中添加一个 Observer,监听了 kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting 和 kCFRunLoopExit 事件,在收到回调时,遍历所有之前放入队列的待处理的任务,然后一一执行。
五、实验
监听App运行的RunLoop状态变化
typedef CF_OPTIONS(CFOptionFlags, CFRunLoopActivity) {
kCFRunLoopEntry = (1UL << 0), // 即将进入Loop
kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers = (1UL << 1), // 即将处理 Timer
kCFRunLoopBeforeSources = (1UL << 2), // 即将处理 Source
kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting = (1UL << 5), // 即将进入休眠
kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting = (1UL << 6), // 刚从休眠中唤醒
kCFRunLoopExit = (1UL << 7), // 即将退出Loop
};
代码:
#import "ViewController.h"
@interface ViewController ()
@property (nonatomic, strong)NSTimer *runLoopObServerTimer;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[self addRunLoopObserver];
[self initData];
}
- (void)initData{
_name = @"Test";
//默认会添加到当前的runLoop中去,不做任何事情,为了让runLoop一直处理任务而不去睡眠
// _runLoopObServerTimer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:0.001 target:self selector:@selector(timerMethod) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
}
- (void)addRunLoopObserver{
//获取当前的CFRunLoopRef
CFRunLoopRef runLoopRef = CFRunLoopGetCurrent();
//创建上下文,用于控制器数据的获取
CFRunLoopObserverContext context = {
0,
(__bridge void *)(self),//self传递过去
&CFRetain,
&CFRelease,
NULL
};
//创建一个监听
static CFRunLoopObserverRef observer;
observer = CFRunLoopObserverCreate(NULL, kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting, YES, 0, &runLoopOserverCallBack,&context);
//注册监听
CFRunLoopAddObserver(runLoopRef, observer, kCFRunLoopCommonModes);
//销毁
CFRelease(observer);
//创建一个监听
static CFRunLoopObserverRef observer2;
observer2 = CFRunLoopObserverCreate(NULL, kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting, YES, 0, &wakeupRunLoopOserverCallBack,&context);
//注册监听
CFRunLoopAddObserver(runLoopRef, observer2, kCFRunLoopCommonModes);
//销毁
CFRelease(observer2);
}
//监听CFRunLoopRef回调函数
static void runLoopOserverCallBack(CFRunLoopObserverRef observer, CFRunLoopActivity activity, void *info){
NSLog(@"runLoopOserverCallBack -> name = kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting - %@", CFRunLoopGetCurrent());
}
static void wakeupRunLoopOserverCallBack(CFRunLoopObserverRef observer, CFRunLoopActivity activity, void *info){
NSLog(@"runLoopOserverCallBack -> name = kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting - %@", CFRunLoopGetCurrent());
}
- (void)timerMethod{
//不做任何事情,为了让runLoop一直处理任务而不去睡眠
}
- (IBAction)actionTwo:(id)sender {
printf("actionTwo");
}
- (IBAction)actionFour:(id)sender {
printf("actionFour");
}
@end
结果分析
在项目启动的时候可以看见初始化构建的runloop,也就是前面说的系统创建的默认loop
仔细分析每一个loop可以了解loop
循环部分:
1、当不触摸设备,设备一分钟更新一次运行循环
2、当用户事件响应,比如点击一个按钮,就会完成一次循环,从唤醒 到 再次进入休眠
3、按理来说,每次循环都会触发自动释放池
4、如果有兴趣可以分析一下打印出来的loop,可以更详细知道loop里都有啥
分析一个loop,前面有描述,可以大概了解一下RunLoop对象中有些什么
Runloop[410:85317] runLoopOserverCallBack ->
//我们监听的loop - kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting
name = kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting - <CFRunLoop 0x170160900 [0x1b843cbb8]>{wakeup port = 0x1e03, stopped = false, ignoreWakeUps = false,
//loop mode
current mode = kCFRunLoopDefaultMode,
//两个公开的common modes
common modes = <CFBasicHash 0x17004bfa0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable set, count = 2,
entries =>
0 : <CFString 0x1b2d00970 [0x1b843cbb8]>{contents = "UITrackingRunLoopMode"}
2 : <CFString 0x1b22484b0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{contents = "kCFRunLoopDefaultMode"}
}
//所有的 common mode items,包含source、timer、observer
common mode items = <CFBasicHash 0x17004beb0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable set, count = 18,
entries =>
0 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170160d80 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -1, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x0, callout = <redacted> (0x193c0bb5c)}}
2 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170162040 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -1, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x170126400, callout = <redacted> (0x198bec0d0)}}
3 : <CFRunLoopObserver 0x170126360 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0x20, repeats = Yes, order = 0, callout = <redacted> (0x1983eb200), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x1700dbeb0>}
4 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170162c40 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource MIG Server> {port = 25095, subsystem = 0x1b2cdd600, context = 0x170033140}}
5 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170163540 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource MIG Server> {port = 27143, subsystem = 0x1b256bf90, context = 0x1700b68c0}}
7 : <CFRunLoopObserver 0x1701260e0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 1999000, callout = <redacted> (0x198698c20), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x100201710>}
8 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170160f00 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -1, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 1, info = 0x3703, callout = <redacted> (0x193c0e370)}}
9 : <CFRunLoopObserver 0x170125fa0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0x1, repeats = Yes, order = -2147483647, callout = <redacted> (0x1983eb38c), context = <CFArray 0x17004e640 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable-small, count = 1, values = (
0 : <0x1001f0048>
)}}
10 : <CFRunLoopObserver 0x170125f00 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 2147483647, callout = <redacted> (0x1983eb38c), context = <CFArray 0x17004e640 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable-small, count = 1, values = (
0 : <0x1001f0048>
)}}
11 : <CFRunLoopObserver 0x170126040 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 2001000, callout = <redacted> (0x1983eb208), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x100201710>}
12 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170161c80 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource MIG Server> {port = 22023, subsystem = 0x1b2cc6ba0, context = 0x0}}
13 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170160b40 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFMachPort 0x1701488d0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, port = 1a03, source = 0x170160b40, callout = <redacted> (0x1954dbebc), context = <CFMachPort context 0x0>}}
14 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x174161380 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x174069040, callout = <redacted> (0x193e6ff34)}}
15 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x174160cc0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFMachPort 0x174148770 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, port = 2203, source = 0x174160cc0, callout = <redacted> (0x1954dbfc8), context = <CFMachPort context 0x0>}}
16 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170161740 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -2, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x17004bd90, callout = <redacted> (0x198bed514)}}
17 : <CFRunLoopObserver 0x174125aa0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 2000000, callout = <redacted> (0x19557de00), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x0>}
18 : <CFRunLoopObserver 0x170125be0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0x20, repeats = Yes, order = 0, callout = runLoopOserverCallBack (0x10002e1fc), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x100208a80>}
19 : <CFRunLoopObserver 0x170125b40 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0x40, repeats = Yes, order = 0, callout = enterRunLoopOserverCallBack (0x10002e238), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x100208a80>}
}
,
modes = <CFBasicHash 0x17004bb80 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable set, count = 5,
entries =>
2 : <CFRunLoopMode 0x170190cf0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{name = UITrackingRunLoopMode, port set = 0x2303, queue = 0x170160cc0, source = 0x1701d88d0 (not fired), timer port = 0x2503,
sources0 = <CFBasicHash 0x17004ccf0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable set, count = 4,
entries =>
0 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170160d80 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -1, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x0, callout = <redacted> (0x193c0bb5c)}}
2 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x174161380 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x174069040, callout = <redacted> (0x193e6ff34)}}
3 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170161740 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -2, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x17004bd90, callout = <redacted> (0x198bed514)}}
6 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170162040 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -1, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x170126400, callout = <redacted> (0x198bec0d0)}}
}
,
sources1 = <CFBasicHash 0x17004ccc0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable set, count = 6,
entries =>
0 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x174160cc0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFMachPort 0x174148770 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, port = 2203, source = 0x174160cc0, callout = <redacted> (0x1954dbfc8), context = <CFMachPort context 0x0>}}
1 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170161c80 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource MIG Server> {port = 22023, subsystem = 0x1b2cc6ba0, context = 0x0}}
2 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170160b40 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFMachPort 0x1701488d0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, port = 1a03, source = 0x170160b40, callout = <redacted> (0x1954dbebc), context = <CFMachPort context 0x0>}}
3 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170162c40 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource MIG Server> {port = 25095, subsystem = 0x1b2cdd600, context = 0x170033140}}
4 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170163540 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource MIG Server> {port = 27143, subsystem = 0x1b256bf90, context = 0x1700b68c0}}
6 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170160f00 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -1, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 1, info = 0x3703, callout = <redacted> (0x193c0e370)}}
}
,
observers = (
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x170125fa0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0x1, repeats = Yes, order = -2147483647, callout = <redacted> (0x1983eb38c), context = <CFArray 0x17004e640 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable-small, count = 1, values = (\n\t0 : <0x1001f0048>\n)}}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x170126360 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0x20, repeats = Yes, order = 0, callout = <redacted> (0x1983eb200), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x1700dbeb0>}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x170125be0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0x20, repeats = Yes, order = 0, callout = runLoopOserverCallBack (0x10002e1fc), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x100208a80>}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x170125b40 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0x40, repeats = Yes, order = 0, callout = enterRunLoopOserverCallBack (0x10002e238), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x100208a80>}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x1701260e0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 1999000, callout = <redacted> (0x198698c20), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x100201710>}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x174125aa0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 2000000, callout = <redacted> (0x19557de00), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x0>}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x170126040 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 2001000, callout = <redacted> (0x1983eb208), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x100201710>}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x170125f00 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 2147483647, callout = <redacted> (0x1983eb38c), context = <CFArray 0x17004e640 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable-small, count = 1, values = (\n\t0 : <0x1001f0048>\n)}}"
),
timers = (null),
currently 583385583 (550429779819) / soft deadline in: 7.68614313e+11 sec (@ -1) / hard deadline in: 7.68614313e+11 sec (@ -1)
},
3 : <CFRunLoopMode 0x170190dc0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{name = GSEventReceiveRunLoopMode, port set = 0x3103, queue = 0x170160e40, source = 0x1701d8c90 (not fired), timer port = 0x3503,
sources0 = <CFBasicHash 0x17004cab0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable set, count = 1,
entries =>
0 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170160d80 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -1, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x0, callout = <redacted> (0x193c0bb5c)}}
}
,
sources1 = <CFBasicHash 0x17004b730 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable set, count = 1,
entries =>
1 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170160fc0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -1, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 1, info = 0x3703, callout = <redacted> (0x193c0e370)}}
}
,
observers = (null),
timers = (null),
currently 583385583 (550429807896) / soft deadline in: 7.68614313e+11 sec (@ -1) / hard deadline in: 7.68614313e+11 sec (@ -1)
},
4 : <CFRunLoopMode 0x170190c20 [0x1b843cbb8]>{name = kCFRunLoopDefaultMode, port set = 0x1f03, queue = 0x170160c00, source = 0x1701d86f0 (not fired), timer port = 0x2103,
sources0 = <CFBasicHash 0x17004bee0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable set, count = 4,
entries =>
0 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170160d80 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -1, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x0, callout = <redacted> (0x193c0bb5c)}}
2 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x174161380 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x174069040, callout = <redacted> (0x193e6ff34)}}
3 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170161740 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -2, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x17004bd90, callout = <redacted> (0x198bed514)}}
6 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170162040 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -1, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x170126400, callout = <redacted> (0x198bec0d0)}}
}
,
sources1 = <CFBasicHash 0x17004bf10 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable set, count = 6,
entries =>
0 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x174160cc0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFMachPort 0x174148770 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, port = 2203, source = 0x174160cc0, callout = <redacted> (0x1954dbfc8), context = <CFMachPort context 0x0>}}
1 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170161c80 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource MIG Server> {port = 22023, subsystem = 0x1b2cc6ba0, context = 0x0}}
2 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170160b40 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFMachPort 0x1701488d0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, port = 1a03, source = 0x170160b40, callout = <redacted> (0x1954dbebc), context = <CFMachPort context 0x0>}}
3 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170162c40 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource MIG Server> {port = 25095, subsystem = 0x1b2cdd600, context = 0x170033140}}
4 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170163540 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource MIG Server> {port = 27143, subsystem = 0x1b256bf90, context = 0x1700b68c0}}
6 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x170160f00 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = No, valid = Yes, order = -1, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 1, info = 0x3703, callout = <redacted> (0x193c0e370)}}
}
,
observers = (
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x170125fa0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0x1, repeats = Yes, order = -2147483647, callout = <redacted> (0x1983eb38c), context = <CFArray 0x17004e640 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable-small, count = 1, values = (\n\t0 : <0x1001f0048>\n)}}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x170126360 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0x20, repeats = Yes, order = 0, callout = <redacted> (0x1983eb200), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x1700dbeb0>}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x170125be0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0x20, repeats = Yes, order = 0, callout = runLoopOserverCallBack (0x10002e1fc), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x100208a80>}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x170125b40 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0x40, repeats = Yes, order = 0, callout = enterRunLoopOserverCallBack (0x10002e238), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x100208a80>}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x1701260e0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 1999000, callout = <redacted> (0x198698c20), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x100201710>}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x174125aa0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 2000000, callout = <redacted> (0x19557de00), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x0>}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x170126040 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 2001000, callout = <redacted> (0x1983eb208), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x100201710>}",
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x170125f00 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 2147483647, callout = <redacted> (0x1983eb38c), context = <CFArray 0x17004e640 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable-small, count = 1, values = (\n\t0 : <0x1001f0048>\n)}}"
),
timers = <CFArray 0x1700b7160 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable-small, count = 1, values = (
0 : <CFRunLoopTimer 0x170161980 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, firing = No, interval = 0, tolerance = 0, next fire date = 583385584 (1.42843509 @ 550464141622), callout = (Delayed Perform) UIApplication _accessibilitySetUpQuickSpeak (0x192da4ab4 / 0x19847d798) (/System/Library/Frameworks/UIKit.framework/UIKit), context = <CFRunLoopTimer context 0x1700734c0>}
)},
currently 583385583 (550429808814) / soft deadline in: 1.43053363 sec (@ 550464141622) / hard deadline in: 1.43053358 sec (@ 550464141622)
},
5 : <CFRunLoopMode 0x174191100 [0x1b843cbb8]>{name = UIInitializationRunLoopMode, port set = 0x3907, queue = 0x174161440, source = 0x1741d8ab0 (not fired), timer port = 0x3c03,
sources0 = <CFBasicHash 0x17404c450 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable set, count = 1,
entries =>
1 : <CFRunLoopSource 0x174161380 [0x1b843cbb8]>{signalled = Yes, valid = Yes, order = 0, context = <CFRunLoopSource context>{version = 0, info = 0x174069040, callout = <redacted> (0x193e6ff34)}}
}
,
sources1 = <CFBasicHash 0x17404c480 [0x1b843cbb8]>{type = mutable set, count = 0,
entries =>
}
,
observers = (
"<CFRunLoopObserver 0x174125aa0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{valid = Yes, activities = 0xa0, repeats = Yes, order = 2000000, callout = <redacted> (0x19557de00), context = <CFRunLoopObserver context 0x0>}"
),
timers = (null),
currently 583385583 (550429860089) / soft deadline in: 7.68614313e+11 sec (@ -1) / hard deadline in: 7.68614313e+11 sec (@ -1)
},
6 : <CFRunLoopMode 0x1741911d0 [0x1b843cbb8]>{name = kCFRunLoopCommonModes, port set = 0x5707, queue = 0x174161980, source = 0x1741d8c90 (not fired), timer port = 0x5803,
sources0 = (null),
sources1 = (null),
observers = (null),
timers = (null),
currently 583385583 (550429861924) / soft deadline in: 7.68614313e+11 sec (@ -1) / hard deadline in: 7.68614313e+11 sec (@ -1)
},
}
}
六、参考
如何保持一个线程一直运行
把runloop开启为常驻
实现测试:
//外部开关
BOOL shouldKeepRunning;
//测试线程
NSThread *myThread;
shouldKeepRunning = YES;
myThread = [[NSThread alloc]initWithBlock:^{
[self doSth];
}];
[myThread start];
//测试线程执行的方法
- (void)doSth {
NSRunLoop *runloop = [NSRunLoop currentRunLoop];
[runloop addPort:[NSMachPort port] forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
//while循环来保证不挂掉,runloop执行到永远~
while (shouldKeepRunning && [runloop runMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode beforeDate:[NSDate distantFuture]]) {
NSLog(@"111");
NSLog(@"%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}
}
//等会在测试线程触发这个方法执行,让runloop唤醒
- (void)doOther {
NSLog(@"22");
}
//按钮事件
- (IBAction)send:(id)sender {
[self performSelector:@selector(doOther) onThread:myThread withObject:nil waitUntilDone:nil];
}
当没有操作按钮的时候,并不会打印测试方法中的 111
当按钮点击的时候
2018-12-04 15:26:40.965699+0800 cyuyan[6501:46603228] 111
2018-12-04 15:26:40.966892+0800 cyuyan[6501:46603228] <NSThread: 0x600000942940>{number = 3, name = (null)}
2018-12-04 15:26:49.882592+0800 cyuyan[6501:46603228] 111
2018-12-04 15:26:49.882885+0800 cyuyan[6501:46603228] <NSThread: 0x600000942940>{number = 3, name = (null)}
多次测试,线程为同一线程。